'Recognizing the need is the primary condition for design.'
Milton Glaser
Unit 1: The engineered world
Learning Aims
A know about engineering processes used to produce modern engineered products
B know about developments in engineering materials and technologies
C understand how engineering contributes to a sustainable future.
Task 1: Review the video below taking short notes / bullet points on any processes used to produce engineering products.
Task 2: Research the following processes in pairs using the internet, write one paragraph per process naming one or more products made with each process.
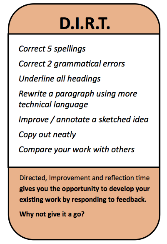
Task 3: Use the D.I.R.T. card below to improve and review your work in pairs.
Task 4: List the safety considerations and any machining techniques used to manufacture these parts.
Task 5: Identify the PPE used and explain why it reduces risk for each process.
Task 6: Once you have completed task 2 - 6 and used the DIRT activities to improve your work to a pass mark or greater use the Link below to take the examplar test.
Learning aim B
B know about developments in engineering materials and technologies
Watch this video first to get a knowledge of the current challenges facing engineering technology today from the Ex head of the MIT
Task 1: Review the short videos below write headings and bulleted notes for each advanced material.
Material / Product Name:
Purpose:
Problem(s) solved:
Advantage over existing materials:
Cost implication:
Social aspect:
Environmental quality:
Inovation or re-design:
Material / Product Name:
Purpose:
Problem(s) solved:
Advantage over existing materials:
Cost implication:
Social aspect:
Environmental quality:
Inovation or re-design:
Material / Product Name:
Purpose:
Problem(s) solved:
Advantage over existing materials:
Cost implication:
Social aspect:
Environmental quality:
Inovation or re-design:
Material / Product Name:
Purpose:
Problem(s) solved:
Advantage over existing materials:
Cost implication:
Social aspect:
Environmental quality:
Inovation or re-design:
Task 2: Move position in the room and pair with someone, discuss your notes and anything you found out that interests you.
Task 3: Use the D.I.R.T. card activities above to help you improve your notes for 5 minutes.(Silent activity)
Task 4: Resume reviewing the remaining videos below while continuing to take bulleted notes.
Material / Product Name:
Purpose:
Problem(s) solved:
Advantage over existing materials:
Cost implication:
Social aspect:
Environmental quality:
Inovation or re-design:
Material / Product Name:
Purpose:
Problem(s) solved:
Advantage over existing materials:
Cost implication:
Social aspect:
Environmental quality:
Inovation or re-design:
Material / Product Name:
Purpose:
Problem(s) solved:
Advantage over existing materials:
Cost implication:
Social aspect:
Environmental quality:
Inovation or re-design:
Task 5: Repeat task 2&3 and then review the last two videos taking notes as you go.
Material / Product Name:
Purpose:
Problem(s) solved:
Advantage over existing materials:
Cost implication:
Social aspect:
Environmental quality:
Inovation or re-design:
Material / Product Name:
Purpose:
Problem(s) solved:
Advantage over existing materials:
Cost implication:
Social aspect:
Environmental quality:
Inovation or re-design:
Task 6: Review all of your notes for this session and then write a short review of your learning using the following questions as headings:
What are the challenges for engineers today?
How can new materials and technoligies help us to solve problems?
Why is sustainability so important?
Can we change the world for the better through Science, Math and Engineering in time to save it and if so, How?
Task 7: Watch the video below and explain in three paragraphs the uses, properties, advantages and disadvantages of Kevlar, Fiberglass and Carbion fiber.
Sustainable Futures
C understand how engineering contributes to a sustainable future.
Task 8: Use the links below to review content related to environmentlal issues.
Practical activity 1: Using woodwork tools to cut and shape an air powered toy boat
Working from the technical drawing below you are to mark out then cut and shape the hull of the boat design using the tools shown.
Task 1: Carefully mark out the shape of the boat hull taking special care to use a rule and pencil
1: Mark a centre line and both construction lines, mark points on the edges.
2: Use construction line marks and points to draw in a semetrical edge for the boat edges.
Task 2: Using a Tenon saw cut away any excess material close to the edge lines. Then (after completing a risk assesment for using the linisher) use the linisher to remove material creating the smooth curve on the edge of the boat hull
Task 3: Set a compass and pencil to 10mm spacing and use it to scribe a line on the underside of the boat hull.
Watch the first 1.45 minutes of the video below to find out how to use a compas and pencil to draw a scribe line.
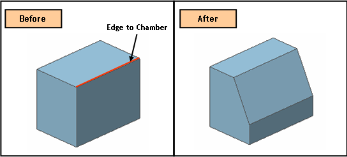
Task 4: Get your tutor to show you how to set the Linisher table to 25 degrees taking care to check it is locked off properly. Then, using the scribed line operate the linisher safely removing material to create the chamfer on the underside of the boat hull.
Project Evaluation:
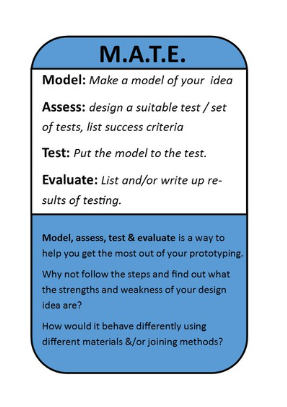
Task 1: In pairs or a small group write a list of evaluation points you could use to assess your project outcome (boat project). E.g. Aesthetics, Use of materials, Finish, Accuracy etc.
Task 2: In your group / pair decide on the evaluation points you will use, discard the rest.
Write these out in a grid with a rating from 0 - 5
e.g.
Aesthetics 0 1 2 3 4 5
Finish 0 1 2 3 4 5